Overview of Ibn Khaldun and His Work
Ibn Khaldun, a 14th-century Arab scholar, is renowned for his seminal work, The Muqaddimah, which laid the foundations for fields like sociology, history, and economics.
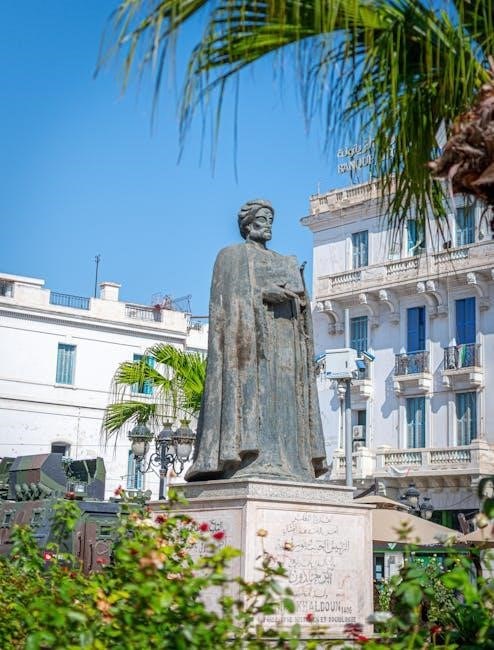

1.1. Biography of Ibn Khaldun
Abd-ar-Raḥmān ibn Khaldūn, born in 1332 in Tunis and died in 1406 in Cairo, was a polymath and one of the most influential Islamic scholars. His full name, Abū Zayd ibn Muḥammad ibn Muḥammad ibn Khaldūn al-Ḥaḍramī, reflects his Yemeni heritage. He excelled in Islamic sciences, history, and philosophy, drawing from his experiences in North African and Andalusian politics. His exile in Algeria inspired his masterpiece, The Muqaddimah.
1.2. The Significance of the Muqaddimah
The Muqaddimah is a monumental work by Ibn Khaldun, establishing the foundations of history, sociology, and economics. It is the most significant Islamic history of the premodern world, offering a comprehensive analysis of human civilization, bedouin life, and societal structures. Its challenging nature and profound insights have made it a cornerstone of Islamic scholarship, influencing modern thought and remaining a vital resource for understanding historical and social dynamics.

Structure and Content of the Muqaddimah
The Muqaddimah begins with an introduction and preliminary remarks, outlining Ibn Khaldun’s methodology and approach to understanding history and human civilization, setting the stage for his analytical framework.
The Muqaddimah opens with an introduction and preliminary remarks, where Ibn Khaldun outlines his methodology for understanding history and human civilization. He emphasizes the importance of critical analysis and objective observation, laying the groundwork for his groundbreaking theories on societal development and historical patterns. This section sets the stage for his comprehensive exploration of human societies and their evolution over time, highlighting his innovative approach to historical and sociological inquiry.
2.2. Key Chapters and Their Focus Areas
The Muqaddimah is structured into key chapters that explore human civilization, bedouin life, urbanization, and the cyclical nature of history. It delves into economics, political leadership, and the role of religion in society. These chapters collectively provide a comprehensive analysis of societal dynamics, offering insights into the rise and fall of empires and the factors influencing cultural and historical development, grounded in empirical observation and critical analysis.
The Philosophy of History in the Muqaddimah
Ibn Khaldun’s philosophy of history introduces a cyclical model of rise and decline, emphasizing social cohesion (asabiyyah) as a determinant of civilizational success, contrasting with traditional chronicles.
3.1. Ibn Khaldun’s Cyclical Theory of History
Ibn Khaldun’s cyclical theory proposes that civilizations rise and fall in a recurring pattern, driven by the decline of social cohesion (asabiyyah). He argued that urbanization and luxury corrupt societies, leading to their eventual collapse. This theory, detailed in the Muqaddimah, challenges traditional historical narratives by emphasizing sociological and economic factors over simplistic chronology.
3.2. The Role of Sociology in Historical Analysis
In the Muqaddimah, Ibn Khaldun integrates sociological insights to analyze history, focusing on social structures, economic conditions, and cultural dynamics. He explores how factors like urbanization, tribal cohesion, and environmental influences shape historical outcomes. This sociological approach provides a deeper understanding of historical events than mere chronological recounting, making the Muqaddimah a pioneering work in the field of historical sociology.

The Muqaddimah as a Foundation of Social Sciences
The Muqaddimah is a cornerstone of social sciences, offering foundational theories in sociology, economics, and political science, and influencing modern scholarship with its comprehensive analytical framework.

4.1. Contributions to Sociology and Ethnography
Ibn Khaldun’s Muqaddimah pioneered sociology and ethnography, analyzing social structures, cultural dynamics, and group solidarity. His theories on urban and rural life, economic systems, and ethnic factors remain foundational in modern social sciences, offering insights into human behavior and societal evolution.
4.2. Economic and Political Insights
In the Muqaddimah, Ibn Khaldun explored economic cycles, taxation impacts, and state formation. He analyzed how economic prosperity influences political stability and vice versa, providing a framework for understanding governance and resource management. His insights remain relevant, linking economic health to the rise and fall of civilizations.

The Muqaddimah in the Context of Islamic Scholarship
The Muqaddimah stands as a cornerstone of Islamic intellectual tradition, blending historical analysis with sociological insight, influencing later Islamic scholarship and historical writing.
5.1. Influence of Islamic Thought on the Work
The Muqaddimah deeply reflects Islamic intellectual traditions, integrating theology, jurisprudence, and philosophy. Ibn Khaldun’s emphasis on empirical observation aligns with Islamic values of knowledge and reason, while his cyclical view of history mirrors Islamic eschatology. The work also incorporates Quranic wisdom and Prophetic traditions, embedding Islamic thought into its sociological and historical frameworks.
5.2. Comparison with Other Islamic Historical Works
While works like The History of al-Tabari focus on chronological narratives, the Muqaddimah stands out for its analytical depth. Unlike al-Masudi’s The Meadows of Gold, Ibn Khaldun’s work introduces sociological theories, offering a unique synthesis of history and social science. This approach sets the Muqaddimah apart as a pioneering work in Islamic scholarship, blending tradition with innovation.
The Muqaddimah and Its Legacy
The Muqaddimah is a foundational work influencing modern historical thought and sociology, leaving a lasting legacy as a pioneering text in Islamic scholarship and global intellectual history.
6.1. Impact on Modern Historical Thought
The Muqaddimah profoundly influenced modern historical thought by introducing sociological and cyclically interpretive approaches to history. Ibn Khaldun’s emphasis on societal structures, economic factors, and cultural dynamics reshaped historical analysis. His ideas preceded modern sociology and remain foundational in understanding historical patterns, offering timeless insights into the evolution of civilizations and human societies.
6.2. Relevance in Contemporary Scholarship
The Muqaddimah remains highly relevant in contemporary scholarship, offering insights into interdisciplinary fields like economics, political science, and sociology. Its cyclical theory of history and sociological analysis continue to inspire modern thinkers, making it a foundational text for understanding complex societal dynamics and historical patterns in both academic and applied research settings.
The Muqaddimah PDF and Its Accessibility
The Muqaddimah is widely available as a PDF, with translations in multiple languages, making it accessible to global scholars. Download sources include academic platforms like Google Scholar and archive.org, offering free access to this foundational text for research and study.
7.1. Sources for Downloading the PDF
The Muqaddimah PDF is widely available online. Google Scholar, archive.org, and ResearchGate provide free access to the text. Translations, such as Franz Rosenthal’s version, can be downloaded. Some platforms require users to copy and paste links into browsers for access. These sources ensure global accessibility for scholars and readers interested in Ibn Khaldun’s groundbreaking work.
7.2. Translations and Their Faithfulness to the Original
Franz Rosenthal’s English translation of the Muqaddimah is praised for its fidelity to Ibn Khaldun’s original Arabic text. It captures the complexity and depth of the work, making it accessible to non-Arabic speakers. While translations inevitably lose some nuances, Rosenthal’s version remains a reliable and faithful representation of Ibn Khaldun’s ideas, ensuring the essence of his philosophical and historical insights is preserved.

Challenges in Interpreting the Muqaddimah
Interpreting the Muqaddimah poses challenges due to its linguistic complexity and cultural context. Its dense Arabic text requires deep understanding of medieval Islamic terminology and historical references.
8.1. Linguistic and Cultural Barriers
The Muqaddimah presents linguistic challenges due to its complex 14th-century Arabic, requiring expertise in medieval Islamic terminology. Cultural nuances and historical references further complicate interpretation, making it difficult for modern readers to grasp without deep contextual knowledge. Additionally, the influence of Islamic thought and societal norms of the time adds layers of complexity, necessitating careful translation and scholarly analysis to preserve the original intent and meaning.
8.2. The Complexity of the Text
The Muqaddimah is renowned for its intricate structure and dense philosophical content, blending history, sociology, and theology. Its dense prose and interconnected ideas demand meticulous study, while its interdisciplinary approach challenges readers to synthesize diverse concepts. This complexity, combined with its historical depth, makes it a formidable work that requires both intellectual rigor and a multidisciplinary perspective to fully comprehend and appreciate its profound insights.

The Muqaddimah’s Influence on Modern Disciplines
Ibn Khaldun’s Muqaddimah has profoundly influenced modern disciplines such as sociology, economics, and political science, establishing foundational theories that remain relevant in contemporary scholarship and research.
9.1. Applications in Economics and Political Science
The Muqaddimah offers insights into economic cycles, taxation impacts, and political stability, influencing modern theories on state formation and resource distribution. Its analysis of societal structures and power dynamics continues to inform political science frameworks, emphasizing the role of institutional legitimacy and economic policies in shaping governance and societal progress across various regions and historical contexts.
9.2. Use in Anthropology and Sociology
The Muqaddimah provides foundational concepts for anthropology and sociology, analyzing societal structures, cultural dynamics, and historical change. Ibn Khaldun’s insights into human civilization, tribal dynamics, and the interplay between nomadic and sedentary life continue to influence contemporary studies of social systems, cultural evolution, and the anthropology of development, offering a timeless framework for understanding human societies and their transformations.
The Muqaddimah remains a cornerstone of Islamic scholarship, offering timeless insights into history, sociology, and human civilization, cementing Ibn Khaldun’s legacy as a pioneering thinker.
10.1. The Enduring Value of the Muqaddimah
The Muqaddimah remains a foundational text in Islamic scholarship, offering profound insights into history, sociology, and economics. Its holistic approach to understanding human civilization continues to inspire contemporary studies. As a PDF, it is widely accessible, ensuring its ideas endure for future generations to explore and learn from Ibn Khaldun’s pioneering work.

10.2. Final Thoughts on Ibn Khaldun’s Legacy
Ibn Khaldun’s legacy is marked by his groundbreaking contributions to social sciences and historical analysis. The Muqaddimah stands as a testament to his intellectual prowess, influencing scholars across disciplines. His work bridges the past and present, making him a timeless figure in Islamic and global intellectual history, ensuring his ideas remain relevant and impactful for centuries to come.
No Responses